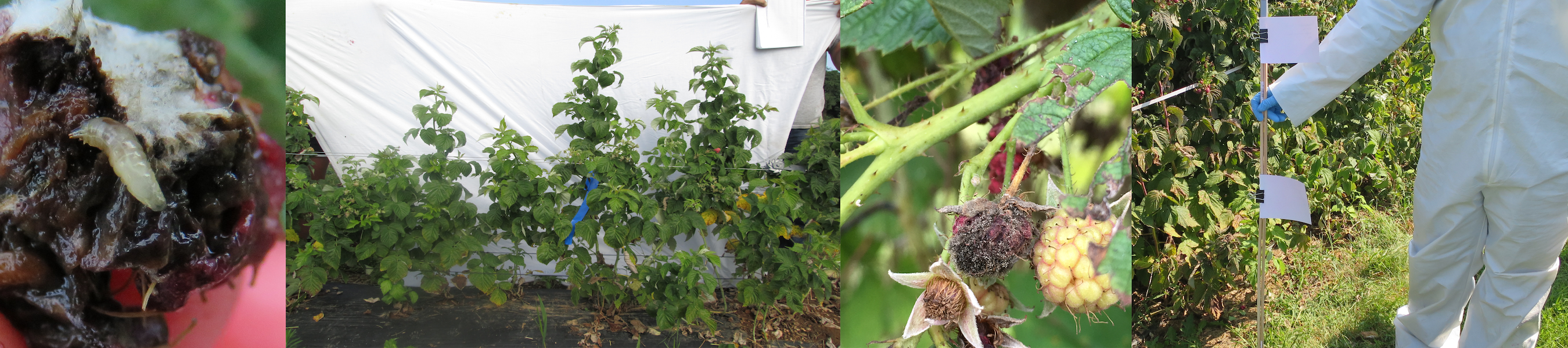
Spotted Wing Drosophila Projects
Spotted wing drosophila, Drosophila suzukii, is a major threat to small and stone fruit production in the U.S., causing direct damage through its egg laying and development of its offspring. The majority of Drosophila species feed on overripe fruit, which spotted wing drosophila can also do, but this species prefers to lay its eggs in ripe fruit and has an egg laying structure that is capable of cutting the skin of thin skinned fruit. For more information about identification and management of this pest, please see resources below.
 Yeast isolated from spotted wing drosophila
Yeast isolated from spotted wing drosophila
Management options for this pest are limited and the impact of spotted wing drosophila on fruit diseases is unknown. Therefore the Hamby lab is working to 1) develop canopy management cultural controls, 2) optimize pesticide spray coverage in Maryland bramble crops, and 3) evaluate crop sterilants for management of spotted wing drosophila and fruit rots.
A long term goal of the Hamby lab is to evaluate how fungal microbes impact and are impacted by spotted wing drosophila, because this is a promising area for developing new attractants for monitoring and management strategies. We are also researching how insect pests may impact plant pathogenic fungi. On a biological level, the nutrition and/or competition from fungi may impact spotted wing drosophila fitness in fruit. The Hamby lab is particularly interested in yeast associations in spotted wing drosophila.
For Hamby lab extension articles on SWD:
Reminders for Monitoring and Managing SWD (pdf)
Does a Crop Sanitizer Reduce Spotted-Wing Drosophila Infestation? (pdf)
Optimizing Spray Coverage in Fall-Bearing Raspberries and Blackberries (pdf)
Cultural Controls for SWD Management in Blueberries and Raspberries (pdf)
If You Can’t Take the Heat, Stay out of the Mulch: How Mulching Practices Affect Spotted Wing Drosophila Survival in Blueberries(pdf)
Fruit Rots and Spotted Wing Drosophila in Fall Bearing Red Raspberries (pdf)
Spotted Wing Drosophila Monitoring and Management (pdf)
For general information on spotted wing drosophila:
http://spottedwing.org/
https://swdmanagement.org/management/
A long term goal of the Hamby lab is to evaluate how fungal microbes impact and are impacted by spotted wing drosophila, because this is a promising area for developing new attractants for monitoring and management strategies. We are also researching how insect pests may impact plant pathogenic fungi. On a biological level, the nutrition and/or competition from fungi may impact spotted wing drosophila fitness in fruit. The Hamby lab is particularly interested in yeast associations in spotted wing drosophila.
For Hamby lab extension articles on SWD:
Reminders for Monitoring and Managing SWD (pdf)
Does a Crop Sanitizer Reduce Spotted-Wing Drosophila Infestation? (pdf)
Optimizing Spray Coverage in Fall-Bearing Raspberries and Blackberries (pdf)
Cultural Controls for SWD Management in Blueberries and Raspberries (pdf)
If You Can’t Take the Heat, Stay out of the Mulch: How Mulching Practices Affect Spotted Wing Drosophila Survival in Blueberries(pdf)
Fruit Rots and Spotted Wing Drosophila in Fall Bearing Red Raspberries (pdf)
Spotted Wing Drosophila Monitoring and Management (pdf)
For general information on spotted wing drosophila:
http://spottedwing.org/
https://swdmanagement.org/management/

